
Geographically weighted regression: the analysis of spatially varying relationships. Locally weighted variation around the localised mean is of interest here, not locally weighted variation around the global mean. Note the use of x (u,v) in this definition. For example, a geographically weighted standard deviation may be defined as: (4) s x (u,v) (x i x (u,v)) 2 w i. GWModel offers a wide range of modeling tools including geographically weighted linear regression, Poisson regression, binomial regression, and even local fitting options including adjustment for local heteroscedasticity, and local ridge regression which is robust to collinearity. However, the geographical weighting approach may be extended beyond this. Stewart, Chris Brunsdon, and Martin Charlton. 11.3.4 Geographically weighted regression. The weighted standard deviation is a useful way to measure the dispersion of values in a dataset when some values in the dataset have higher weights than others. Method of estimation for the variance components in the random effects model, one of "swar" (default), "amemiya", "walhus", or "nerlove"īisquare: wgt = (1-(vdist/bw)^2)^2 if vdist Shunsuke Managiįotheringham, A.

Panel model transformation: (c("within", "random", "pooling")) The effects introduced in the model, one of "individual" (default), "time", "twoways", or "nested" The power of the Minkowski distance, default is 2, i.e. If TRUE, adaptive distance bandwidth is used, otherwise, fixed distance bandwidth. Answer (1 of 2): The formula for weighted standard deviation is: where N is the number of observations.

The optimal bandwidth, either adaptive or fixed distance Spatial*DataFrame on which is based the data, with the "ID" in the index + XkĪ vector of the two indexes: (c("ID", "Time"))
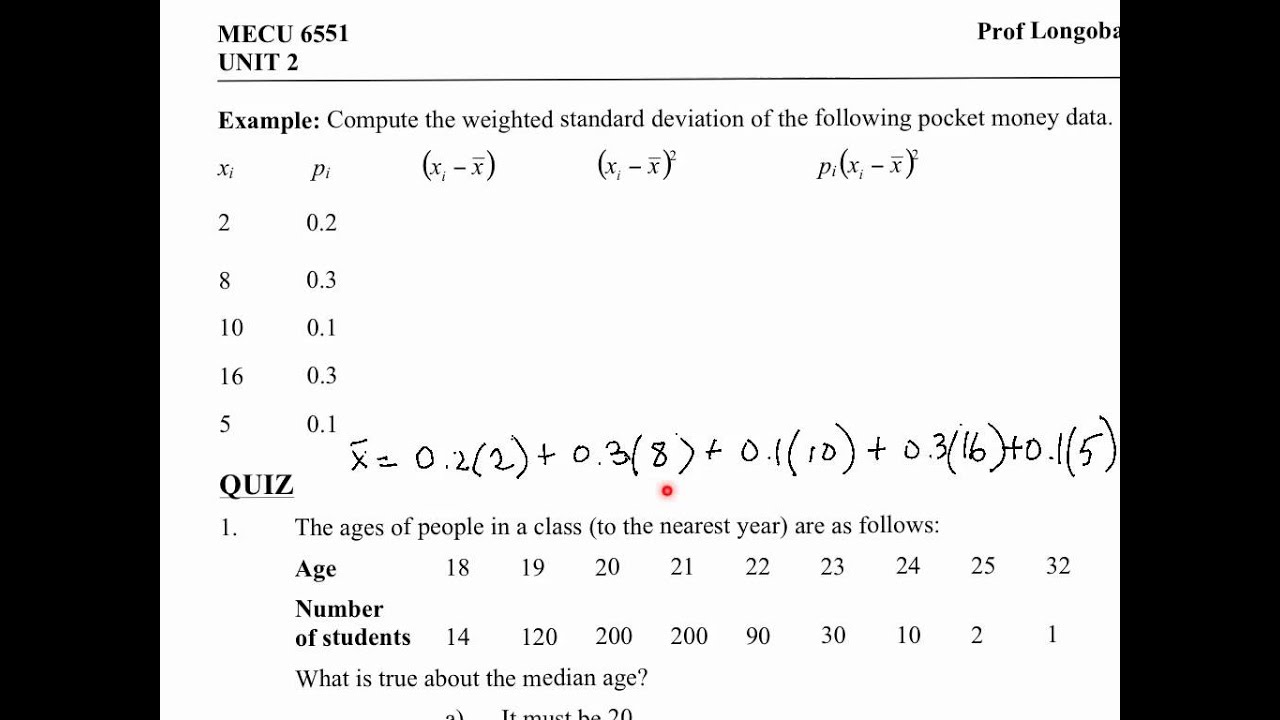
There seem to be solution available for weighted mean (groupby weighted average and sum in pandas dataframe) but none for weighted standard deviation. To investigate this inconsistency, this study introduces the peak deviation coefficient to describe this phenomenon. GWPR ( formula, data, index, SDF, bw = NULL, adaptive = FALSE, p = 2, effect = "individual", model = c ( "pooling", "within", "random" ), thod = "swar", kernel = "bisquare", longlat = FALSE ) I want to group on type and then calculate weighted mean and weighted standard deviation. The ridership of a metro station during a city’s peak hour is not always the same as that during the station’s own peak hour.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
